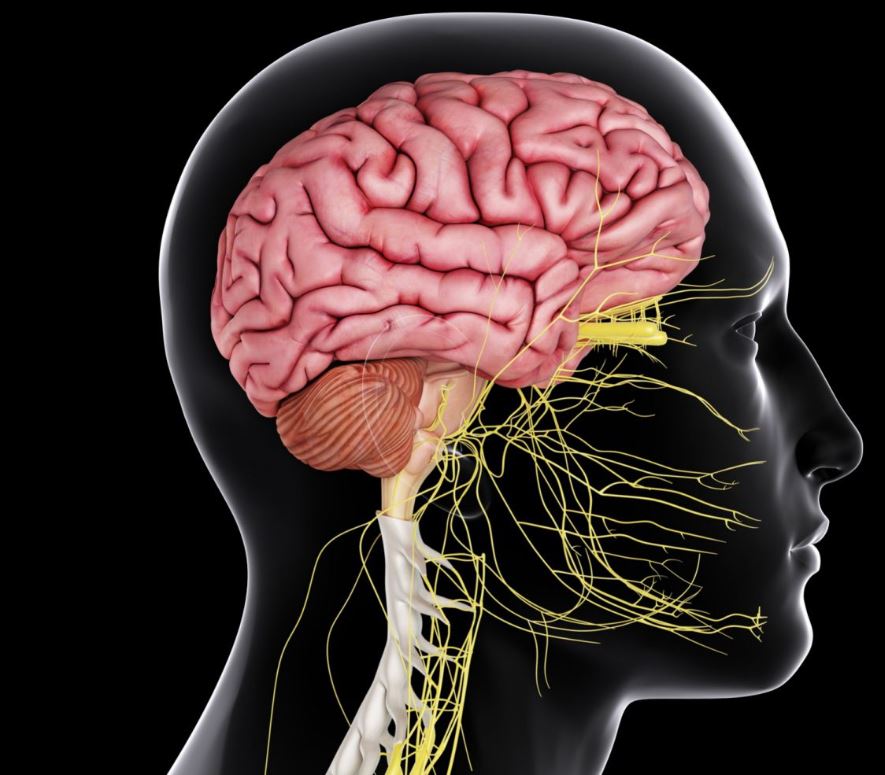
The nervous system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that coordinates and controls many functions in the body. Its primary role is to transmit signals between different parts of the body and to integrate and process sensory input from the environment.
Here are some of the key functions of the nervous system:
1. Sensory input: The nervous system receives sensory information from the environment through the five senses (sight, sound, touch, taste, and smell) and sends this information to the brain for processing.
2. Integration: The nervous system integrates sensory information and processes it to determine an appropriate response.
3. Motor output: The nervous system sends signals to muscles and glands to initiate movement or to secrete hormones.
4. Regulation of bodily functions: The nervous system regulates many bodily functions, such as heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, and respiration.
5. Coordination and balance: The nervous system coordinates movements and helps to maintain balance and stability.
6. Cognitive function: The nervous system plays a key role in cognitive function, including learning, memory, and problem-solving.
7. Emotions and behavior: The nervous system regulates emotions and behavior through the release of neurotransmitters that affect mood and motivation.
Overall, the nervous system is critical for the proper functioning of the body and plays a key role in maintaining homeostasis and adapting to changes in the environment.
Dysregulated Nervous System
Here are some signs that the nervous system may be dysregulated:
1. Anxiety: Dysregulation of the nervous system can lead to feelings of anxiety, nervousness, and fear.
2. Depression: Dysregulation of the nervous system can also lead to symptoms of depression, such as sadness, hopelessness, and low energy.
3. Mood swings: Dysregulation of the nervous system can cause sudden and intense changes in mood, such as irritability, anger, and frustration.
4. Insomnia: Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep can be a sign of nervous system dysregulation.
5. Fatigue: Dysregulation of the nervous system can lead to feelings of fatigue, low energy, and exhaustion.
6. Digestive issues: Nervous system dysregulation can also cause digestive problems such as nausea, bloating, and abdominal pain.
7. Headaches: Frequent headaches or migraines can be a sign of nervous system dysregulation.
8. Sensitivity to stimuli: Dysregulation of the nervous system can cause heightened sensitivity to light, sound, and other stimuli.
9. Chronic pain: Nervous system dysregulation can contribute to chronic pain, such as fibromyalgia or chronic fatigue syndrome.
10. Difficulty concentrating: Dysregulation of the nervous system can make it difficult to concentrate, remember things, or process information.
Behaviours that can dysregulate the nervous system
Here’s a list of ten behaviors that can dysregulate the nervous system:
1. Chronic stress: Prolonged exposure to stress can cause dysregulation of the nervous system, leading to a variety of physical and mental health problems.
2. Lack of sleep: Insufficient or poor-quality sleep can also dysregulate the nervous system and lead to fatigue, mood swings, and other symptoms.
3. Substance abuse: The use of drugs or alcohol can alter the functioning of the nervous system, leading to dysregulation and potentially serious health problems.
4. Poor diet: Eating a diet that is high in sugar, processed foods, and unhealthy fats can cause inflammation and contribute to dysregulation of the nervous system.
5. Lack of exercise: A sedentary lifestyle can also dysregulate the nervous system and contribute to anxiety, depression, and other symptoms.
6. Trauma: Experiencing trauma can lead to dysregulation of the nervous system and result in symptoms such as anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
7. Chronic pain: Living with chronic pain can also dysregulate the nervous system and cause a range of physical and emotional symptoms.
8. Overstimulation: Exposure to too much noise, light, or other stimuli can cause dysregulation of the nervous system and lead to feelings of anxiety, stress, or overwhelm.
9. Poor social support: A lack of social support can also dysregulate the nervous system and lead to feelings of loneliness, isolation, and depression.
10. Lack of self-care: Neglecting basic self-care practices such as exercise, healthy eating, and stress management can dysregulate the nervous system and lead to a range of health problems.
How to regulate your nervous system
There are several ways to regulate the nervous system, and here are some examples:
1. Deep breathing: Engaging in deep breathing exercises can help to calm the nervous system and reduce stress levels. Try inhaling for a count of four, holding for a count of four, and exhaling for a count of four.
2. Mindfulness meditation: Practicing mindfulness meditation can help to regulate the nervous system by bringing awareness to the present moment and reducing stress and anxiety.
3. Exercise: Regular exercise, such as aerobic activity, can help to regulate the nervous system by reducing stress hormones and increasing feel-good endorphins.
4. Yoga: Practicing yoga can help to regulate the nervous system by incorporating breathing techniques and physical postures that promote relaxation and stress reduction.
5. Social support: Maintaining positive relationships and social support networks can help to regulate the nervous system by reducing feelings of isolation and loneliness.
5. Therapy: Working with a mental health professional pm, can help to regulate the nervous system by providing support, guidance, and strategies for managing stress and anxiety.
6. Healthy eating: Eating a balanced and nutritious diet can help to regulate the nervous system by providing the body with the nutrients it needs to function properly.
7. Sleep: Getting adequate and restful sleep is crucial for regulating the nervous system, as it allows the body to rest and restore itself.
Overall, engaging in self-care practices that promote relaxation, stress reduction, and physical health can help to regulate the nervous system and promote overall well-being
