Brain waves are electrical patterns of activity generated by the neurons in the brain.
These electrical signals are measured using an electroencephalogram (EEG), which records the voltage fluctuations caused by the firing of neurons.
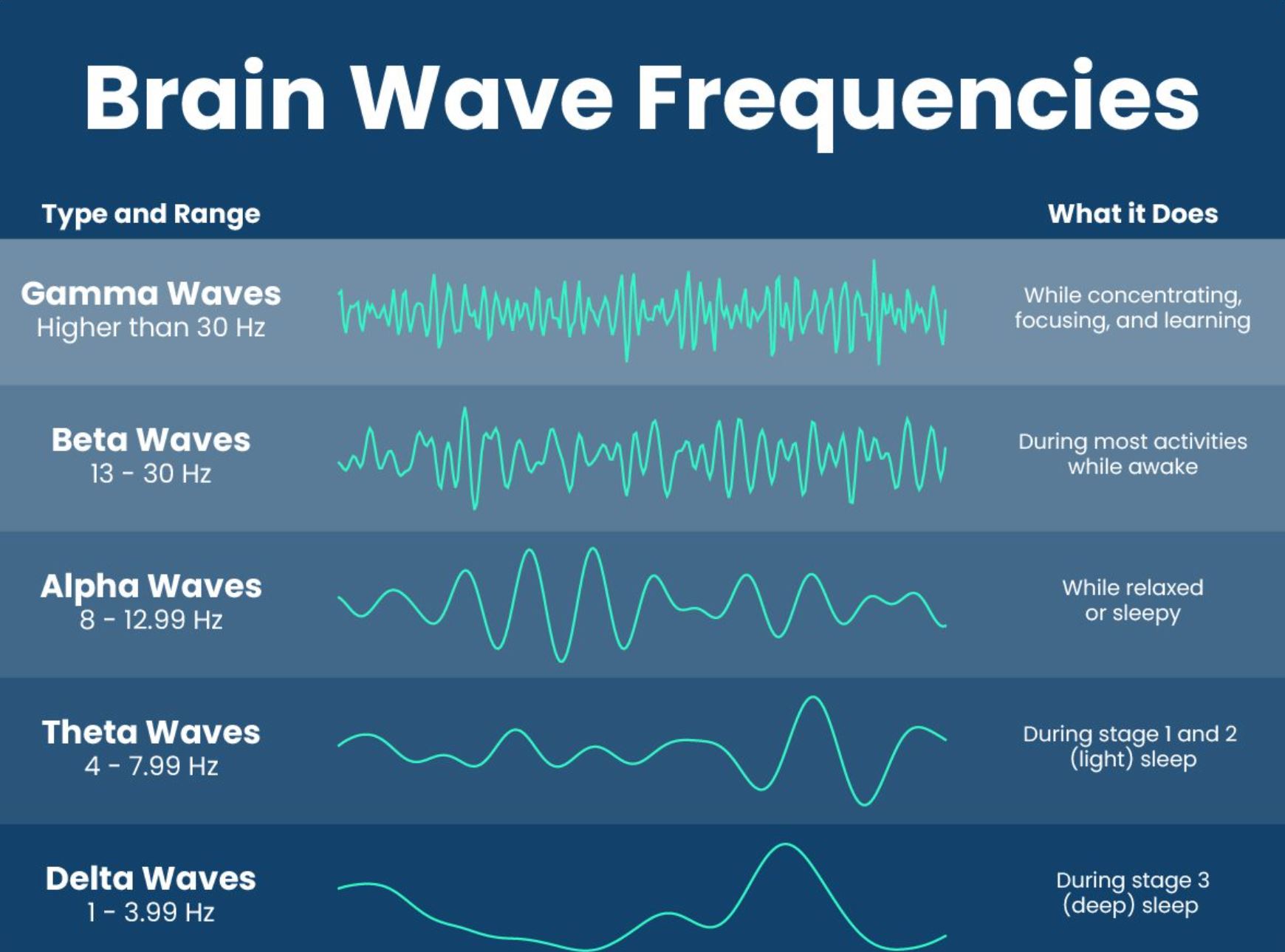
There are different types of brain waves that can be observed on an EEG, and they are classified based on their frequency and amplitude.
The main types of brain waves are:
1. Delta Waves: These waves have a frequency of 0.5-4 Hz and high amplitude. They are typically observed during deep sleep and are associated with restorative processes such as physical healing and tissue repair.
2. Theta Waves: These waves have a frequency of 4-8 Hz and lower amplitude than delta waves. They are associated with a state of relaxation, drowsiness, and light sleep. Theta waves are also observed during meditation and hypnosis.
3. Alpha Waves: These waves have a frequency of 8-12 Hz and even lower amplitude than theta waves. They are observed when a person is awake but relaxed, and are associated with a state of calmness and alertness.
4. Beta Waves: These waves have a frequency of 13-30 Hz and even lower amplitude than alpha waves. They are associated with a state of active mental engagement, such as problem-solving, decision-making, and focused attention.
5. Gamma Waves: These waves have a frequency of 30-100 Hz and are associated with high-level cognitive processing, such as perception, memory, and consciousness.
The different types of brain waves are not exclusive to one another and can be observed simultaneously in different areas of the brain.
The patterns of brain waves can provide insights into brain function and can be used to diagnose and treat neurological disorders.
Brain waves upon waking up
The order of brain waves upon waking up can vary depending on the individual, but a general progression is as follows:
1. Delta Waves: During deep sleep, the brain produces delta waves with a frequency of 0.5-4 Hz and high amplitude.
2. Theta Waves: As a person begins to wake up, the brain waves transition to theta waves with a frequency of 4-8 Hz and lower amplitude.
3. Alpha Waves: As the person becomes more relaxed and alert, the brain waves shift to alpha waves with a frequency of 8-12 Hz and even lower amplitude.
4. Beta Waves: Finally, as the person becomes fully awake and alert, the brain waves transition to beta waves with a frequency of 13-30 Hz and even lower amplitude.
It’s important to note that the progression of brain waves may not be linear and can vary depending on factors such as sleep quality, sleep stage, and individual differences
Please visit my website to see my services and book a COMPLIMENTARY CALL.
